Design of dissimilar material joint for defect-free multi-material add…
page information
Writer InssTek 작성일25-02-18 15:55related link
-
 https://www.linkedin.com/posts/insstek_materialabrresearchabrwithabrin…
238 times connection
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/insstek_materialabrresearchabrwithabrin…
238 times connection
body text
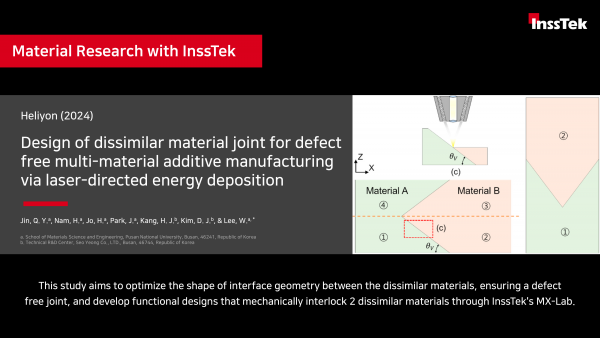
Design of dissimilar material joint for defect-free multi-material additive manufacturing via laser-directed energy deposition
Summary:
• This study aims to optimize the shape of interface geometry between the dissimilar materials, ensuring a defect
free joint, and develop functional designs that mechanically interlock 2 dissimilar materials through InssTek's MX-Lab.
• In this study, AISI 316L stainless steel and Inconel 625 (Nickel alloy) were joined into various structures using the LDED.
•And tensile test was chosen to evaluate the performance of the various designs. This test is conducted to assess the structural characteristics and performance of both the V-type and anchor joints.
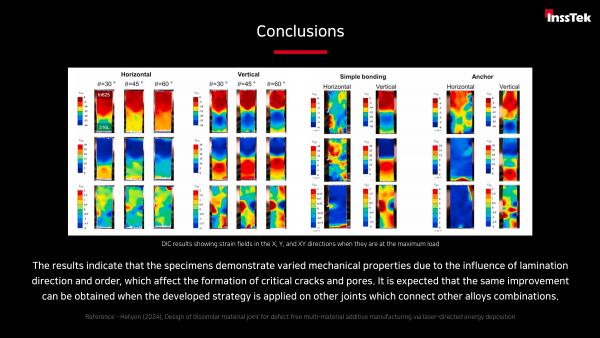
• The results indicate that the specimens demonstrate varied mechanical properties due to the influence of lamination direction and order, which affect the formation of critical cracks and pores.
•It is expected that the same improvement can be obtained when the developed strategy is applied on other joints which connect other alloys combinations.
Reference:
- https://www.cell.com/heliyon/fulltext/S2405-8440(24)05697-4
- https://insstek.com/products/mx-lab
#Metallurgy #Alloy #Bimetal #DissimilarMaterial #MaterialResearch #Alloyresearch #AdditiveManufacturing #AM #DED #3Dprinter
Summary:
• This study aims to optimize the shape of interface geometry between the dissimilar materials, ensuring a defect
free joint, and develop functional designs that mechanically interlock 2 dissimilar materials through InssTek's MX-Lab.
• In this study, AISI 316L stainless steel and Inconel 625 (Nickel alloy) were joined into various structures using the LDED.
•And tensile test was chosen to evaluate the performance of the various designs. This test is conducted to assess the structural characteristics and performance of both the V-type and anchor joints.
• The results indicate that the specimens demonstrate varied mechanical properties due to the influence of lamination direction and order, which affect the formation of critical cracks and pores.
•It is expected that the same improvement can be obtained when the developed strategy is applied on other joints which connect other alloys combinations.
Reference:
- https://www.cell.com/heliyon/fulltext/S2405-8440(24)05697-4
- https://insstek.com/products/mx-lab
#Metallurgy #Alloy #Bimetal #DissimilarMaterial #MaterialResearch #Alloyresearch #AdditiveManufacturing #AM #DED #3Dprinter
Comments list
No comments have been registered.